Diabetes, a common condition affecting a significant portion of the population, isn’t just about blood sugar levels. This condition can impact your whole body, and the eyes are no exception to this. Diabetes increases the risk of eye conditions like glaucoma, cataracts, and diabetic retinopathy—especially if left unmanaged.
This is why diabetic eye exams are so important. During a diabetic eye exam, your optometrist will dilate your pupils and thoroughly examine the delicate systems at the back of your eye, taking careful note of any changes or irregularities. It offers a way to preserve your vision and protect yourself against conditions that can be difficult, or impossible, to self-diagnose.
What Is Diabetes?
Your pancreas, a small organ located behind the stomach, produces a hormone called insulin. This is responsible for regulating the blood sugar levels in your body. Without insulin, your body is unable to properly process the sugars from the food you eat.
Diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body can no longer properly use this insulin, which quickly throws things into disarray. There are 2 types of diabetes:
- Type 1, which is an autoimmune disorder that leads to the immune system attacking and destroying the insulin-producing cells
- Type 2, which occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin.
Both types of diabetes can quickly lead to elevated blood sugar levels, which can cause significant complications throughout the rest of your body.
How Diabetes Affects the Body
When you constantly have higher levels of blood sugar, it puts additional strain on the blood vessels throughout the body. High blood sugar, known as hyperglycemia, can damage these vessels, your nerves, your organs, and more. This increases the risk of:
- Heart disease
- Kidney failure
- Nerve damage
- Stroke
However, there’s one body part often overlooked—your eyes. Prolonged periods of high blood sugar can have a significant effect on your eyes, increasing the risk of conditions like cataracts and glaucoma. One of these conditions is diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic Retinopathy: What Is It?
At the back of your eyes, there is a clump of light-sensitive cells called the retina. This is what helps you see, converting light into signals that your brain interprets. When blood sugar levels are too high for extended periods, it can cause damage to the small blood vessels in the retina, leading to a condition known as diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common type of eye disease associated with diabetes and one of the leading causes of blindness in adults. It typically affects both eyes and can be categorized into two types:
- Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy: This early stage involves weakened blood vessels leaking fluid or blood into the retina, causing blurred vision.
- Proliferative diabetic retinopathy: In advanced stages, new blood vessels may grow in the retina, but they are fragile and can easily leak, leading to severe vision loss or even blindness.
Diabetic retinopathy can quickly lead to permanent vision loss, making it crucial to recognize the early signs of the condition.
Signs of Diabetic Retinopathy
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetic retinopathy early is crucial. Here are some common signs to watch for:
- Blurred vision
- Floaters (small dark spots or strings that float in your vision)
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Dark or empty areas in your vision
- Partial or total loss of vision
Fortunately, these signs can be caught long before they pose a serious risk by scheduling a diabetic eye exam.
Why Are Diabetic Eye Exams Important?
Diabetic retinopathy is a silent disease that often has no obvious symptoms until it reaches advanced stages. This is why regular diabetic eye exams are crucial for early detection and treatment. During an eye exam, your eye doctor will check for signs of retinal damage, including:
- Swelling
- Changes in blood vessels
- Bleeding
- Fluid buildup in the retina
If detected early enough, your optometrist will intervene and give you advice on properly managing your diabetes to slow, or stop, the progression of your condition.
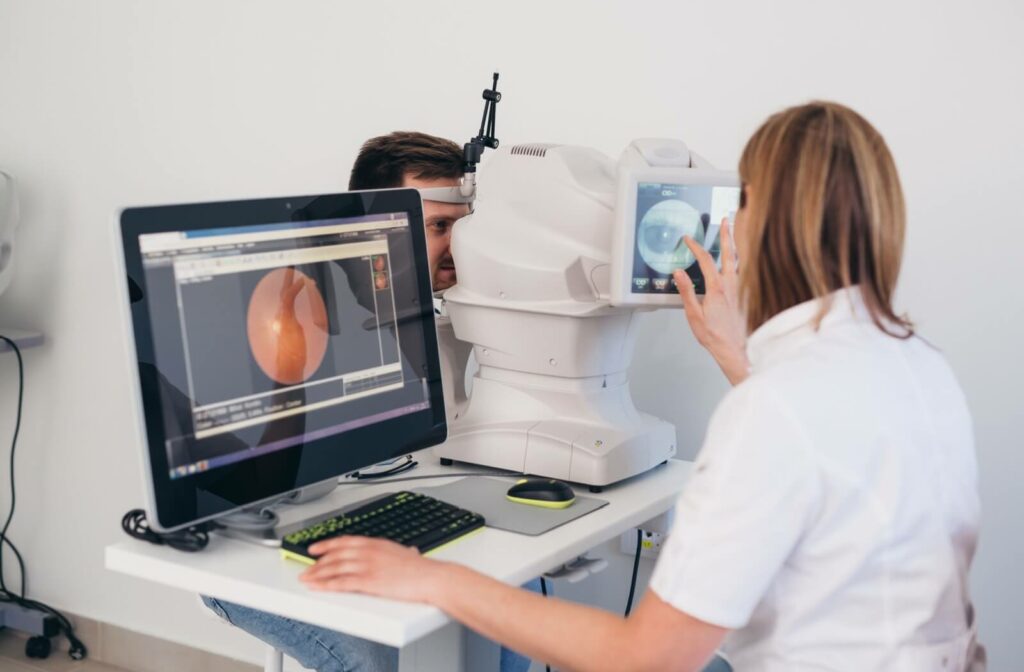
What to Expect During a Diabetic Eye Exam
Diabetic eye exams are similar to regular eye exams. Your optometrist will check your vision, see how your eyes align, and check the overall health of your eyes.
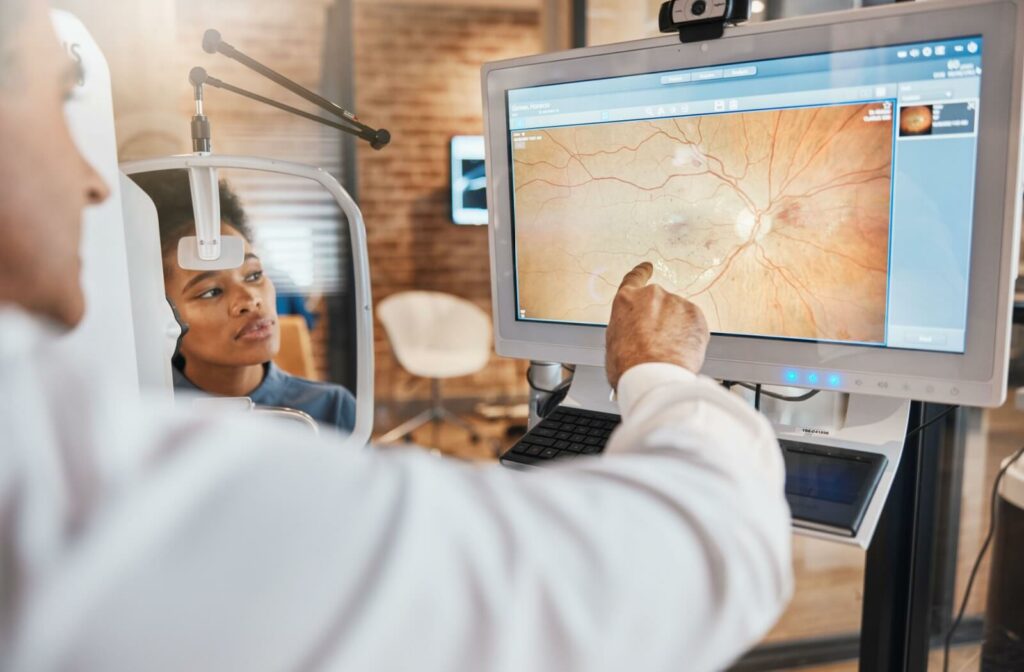
However, diabetic eye exams take it one step further and perform additional tests to check specifically for signs of diabetes-related conditions. Here at McCauley Celin Eyecare Associates, we’ll use:
- EIDON Fundus Photography, to gain an in-depth image of your retinas
- Optical Coherence Tomography, to gain a cross-sectional image of your eyes
If you have diabetes, you should be scheduling diabetic eye exams at least once a year, or more often if recommended by your optometrist.
Book Your Next Eye Exam
Managing diabetes involves more than just monitoring blood sugar levels—it requires comprehensive care through regular eye exams. So, come visit our team at McCauley Celin Eyecare Associates. Our team is here to help you preserve your vision and maintain your overall health, so book an appointment with us today!